5-year curriculum
Bishkek International Medical Institute offers a 5-year program. The curriculum The curriculum is designed to provide students with an appropriate foundation for to complete the General Medicine degree program at BMMI.
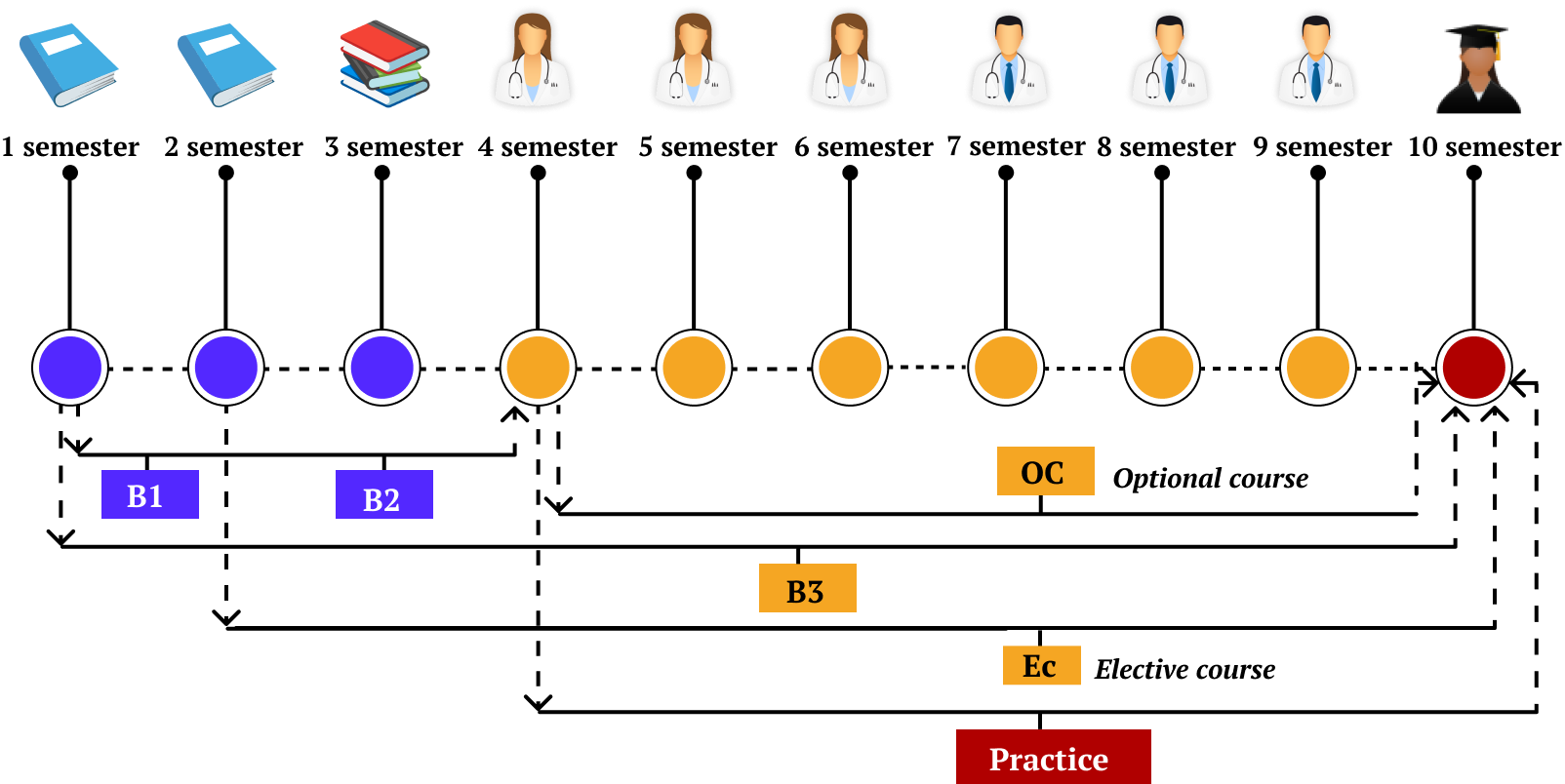
Bishkek International Medical Institute offers a 5-year program. The curriculum The curriculum is designed to provide students with an appropriate foundation for to complete the General Medicine degree program at BMMI.
